United States

|
The International Children's Heart Fund includes
initiatives in the United States. There are clearly needs in our own
country. Past projects included sponsoring a food trailer to
local food pantries in Worcester, MA. |




Some Music from Youtube
you may be interested in listening to:
Whitney Houston singing
the National Anthem in 1991
Ray Charles - Oh
Beautiful America
Simon and Garfunkel -
America
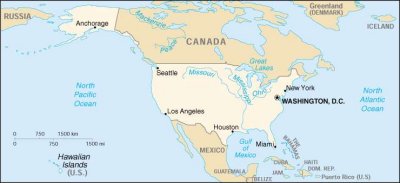
| Location: | North America, bordering
both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between
Canada and Mexico 38 00 N, 97 00 W |
| Population: | 278,058,881 (July 2001 est.) |
| Area: | total: 9,629,091 sq
km land: 9,158,960 sq km water: 470,131 sq km note: includes only the 50 states and District of Columbia about one-half the size of Russia; about three-tenths the size of Africa; about one-half the size of South America (or slightly larger than Brazil); slightly larger than China; about two and one-half times the size of Western Europe |
| Climate: | mostly temperate, but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the great plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the Great Basin of the southwest; low winter temperatures in the northwest are ameliorated occasionally in January and February by warm Chinook Winds from the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains |
| Terrain: | vast central plain, mountains in west, hills and low mountains in east; rugged mountains and broad river valleys in Alaska; rugged, volcanic topography in Hawaii |
| Elevation: | lowest point: Death
Valley -86 m highest point: Mount McKinley 6,194 m |
| Natural resources: | coal, copper, lead, molybdenum, phosphates, uranium, bauxite, gold, iron, mercury, nickel, potash, silver, tungsten, zinc, petroleum, natural gas, timber |


