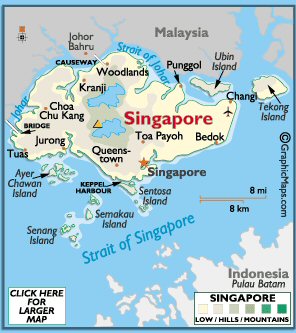
Singapore
2012
This strategic island called Singapore was first inhabited by regional fishermen and pirates, and later became part of the Sumatran Empire of Srivijaya.
European control of the Malaysian area began in the 16th century, and in 1819, Singapore was founded as a British trading colony, and was once the site of one of Britain's most important naval bases. Malaysia itself was formed in 1963 when Singapore and the states of Sabah and Sarawak joined the Peninsular Malaysia Federation. However, Singapore left in 1965 to become a separate nation.
This modern economic powerhouse's is one of the busiest in the world, and Singapore has become a major worldwide banking, ship building and petroleum center.
In the last few decades, this melting pot of cultures has moved on to the A List for international travelers, and is today one of the most sophisticated tourist destinations on the planet.
A bridge and causeway connect Singapore to the Malaysia mainland, and speaking of land, because of the aggressive current patterns of the Strait of Singapore, there are much-needed and on-going land reclamation projects.
| Location: |
01º 22' N, 103º 48' E Singapore is in both the northern and eastern hemispheres. The country is immediately north of the Equator, and positioned off the southern edge of the Malay Peninsula between Malaysia and Indonesia. It's separated from Malaysia by the Strait of Johar, and from Indonesia by the Strait of Singapore. |
| Area: |
(land) 263 sq miles (683 sq km) (water) 4 sq miles (10 sq km) (TOTAL) 267 sq miles (693 sq km) |
| Climate: |
Positioned just north of the Equator, Singapore's location and maritime
exposure produces a climate characterized by uniform temperatures, high
humidity and numerous sunshiny days. The Monsoon (rainy) seasons are (April - May) and (December - March). Windy conditions prevail, January through February. Its average daily maximum temperature is just over 88° F, with a relative humidity near 75%. |
| Terrain: |
The country of Singapore consists of one main island and over 60 small
islands (islets). The middle of the main island contains a number of rounded hills; west and southwest the land is a series of low ridges, while east and southeast, the land is generally flat. Singapore is drained by a large number of narrow and short streams, some of which flow into the sea through mangrove swamps, or estuaries. Water reservoirs cover parts of the central area, as there are no significant lakes or rivers. |
| Elevation: |
JBukit Timah - 545 ft. (166 m) Strait of Singapore - (0 ft.) (0 m) |


